Dog emotions are more complex than many people once believed. Research in animal behavior and neuroscience shows that dogs experience a wide range of feelings, from joy and excitement to anxiety and fear. What makes this especially powerful is their dog emotional intelligence—the ability to interpret human signals and adjust their behavior accordingly.
For U.S. pet owners, this understanding reshapes how we see the dog human bond. Dogs don’t just live alongside us; they actively read us. They monitor our facial expressions, tone of voice, posture, and daily rhythms. Over time, this constant observation forms a feedback loop of emotional connection that benefits both species.
Understanding how dogs process emotion helps us respond more thoughtfully. It also improves training outcomes, household harmony, and long-term well-being.
Recognizing Affection and Emotional Signals in Dogs
A core part of understanding dog emotions is recognizing how dogs express affection. Their dog perception of love is not abstract. It is behavioral and physiological.
Dogs show attachment through proximity, relaxed body posture, soft eye contact, tail movement, and leaning into touch. They may follow you from room to room, rest near your feet, or bring a favorite toy as an invitation to engage. These are not random behaviors; they are clear emotional cues.
Reading dog body language is essential. A loose, wagging tail at mid-height signals comfort. Relaxed ears and soft blinking suggest safety. A tense posture or avoidance, on the other hand, indicates stress. The key is context. The same tail wag can mean excitement or anxiety depending on speed, height, and body tension.
Canine empathy plays a role here. Dogs often mirror our energy levels. If you move calmly, they settle. If you rush, they may become alert or agitated. This mirroring reflects emotional attunement.
If you want to express affection in ways dogs naturally understand, consider learning more about dog-centered communication. Discover practical ways to connect with your pet by exploring How to Tell My Dog I Love Him: Dog Language. Small adjustments—like lowering your voice, slowing your movements, and respecting personal space—can significantly strengthen connection.
How Dogs Sense Human Mood and Sadness

Many owners ask: can dogs sense sadness? Evidence suggests they can detect emotional shifts through multiple channels.
Dogs rely heavily on scent. Human emotional states trigger subtle hormonal and chemical changes, which alter body odor. A dog’s powerful olfactory system can detect these changes quickly. They also analyze facial tension, eye focus, breathing patterns, and vocal tone.
When exploring whether Can Dogs Sense Sadness, experts highlight behavioral responses such as increased closeness, gentle nudging, pawing, or resting their head on a person’s lap. These dog behavior cues suggest attempts at engagement and reassurance.
This doesn’t mean dogs intellectually understand complex life circumstances. Rather, they recognize emotional shifts and respond instinctively. That instinctive response is part of how dogs understand human feelings.
In many U.S. households, dogs act as informal emotional stabilizers. Their presence can slow breathing, reduce heart rate, and promote calm interaction. This dynamic reflects human-canine co-regulation—a shared emotional balancing process where both nervous systems influence each other.
A soft example can be seen in educational resources like PawChamp, where discussions around canine empathy emphasize science-based insight rather than exaggeration. The takeaway is simple: dogs respond to what they perceive, and they perceive more than we often realize.
Communication Without Words: How Dogs Use Non-Verbal Signals
Effective dog communication is primarily nonverbal. While dogs can learn dozens of verbal cues, they are far more responsive to posture, tone, rhythm, and timing.
Your dog tone of voice matters more than specific vocabulary. A warm, steady tone signals safety. A sharp or inconsistent tone can create confusion. Dogs also observe breathing patterns and muscle tension. Subtle shifts in your shoulders or jaw can change how a dog interprets your state.
Dogs send their own dog emotional cues continuously. These include:
- Lip licking when stressed
- Yawning in tense situations
- Turning their head away to avoid conflict
- Slow blinking as a calming signal
These are often misinterpreted as disobedience or distraction. In reality, they are forms of emotional signaling.
Understanding nonverbal cues strengthens trust. When owners respond appropriately—pausing during stress, lowering intensity during play, or providing space when needed—dogs feel understood. That understanding reinforces the bond.
Consistent emotional clarity also supports nervous system regulation for both dog and owner. Calm communication reduces chronic stress and supports long-term behavioral stability.
Quality Time and Routines That Strengthen Emotional Bonds
The phrase quality time with dogs is often misunderstood. It doesn’t require elaborate activities. It requires presence.
Focused walks without phone distractions allow dogs to explore safely while checking back in with you. Short training sessions reinforce the dog training bond through positive reinforcement and shared attention. Even quiet time on the couch can deepen attachment when it feels secure and unhurried.
Predictable routines are especially powerful. Dogs thrive on structure. Regular feeding times, walk schedules, and sleep routines create emotional stability. This predictability reduces anxiety and supports a strong dog human connection.
Structured play also enhances emotional resilience. Games like scent work or basic obedience exercises engage cognitive skills and reinforce cooperative interaction. This strengthens trust and communication simultaneously.
Consistency builds confidence. Confidence reduces unwanted behaviors rooted in insecurity or confusion.
Supporting Your Dog’s Emotional Well-Being with Positive Practices
Supporting dog emotions goes beyond affection. It involves proactive emotional care.
Canine calm routines are foundational. This includes consistent sleep patterns, safe resting spaces, and gentle transitions between activities. Avoid sudden loud corrections. Instead, guide behavior with clarity and reward desired responses.
Movement is equally important. Daily physical activity regulates energy levels and improves mood stability. Balanced exercise reduces stress-related behaviors such as excessive barking or pacing.
Mental enrichment also matters. Puzzle toys, scent exploration, and training games stimulate the brain and prevent boredom-driven anxiety.
Owners should also monitor their own emotional state. Dogs respond to us in real time. If stress levels in the household rise, dogs often absorb that tension. Practicing self-awareness contributes to better dog support for human emotions and vice versa.
The science behind this reciprocal process is increasingly recognized. Emotional synchronization between humans and dogs reflects shared evolutionary history and close domestication patterns. Dogs evolved alongside humans, adapting to our communication style and emotional rhythms.
In practical terms, this means small improvements in how we interact can produce measurable changes in behavior and well-being.
Final Thoughts
Dog emotions are real, measurable, and influential. Through strong dog emotional intelligence, dogs interpret facial expressions, scent changes, posture shifts, and vocal tone. They respond not with abstract reasoning, but with adaptive behavior shaped by thousands of years of partnership with humans.
By learning to read dog body language, understanding canine empathy, and committing to consistent calm routines, owners strengthen the dog human bond in lasting ways.
The result is not just better behavior. It is deeper mutual trust, improved emotional balance, and a relationship built on clarity and respect.
Dogs are always communicating. When we learn to listen without words, the connection becomes stronger than ever.
Public Opinion’s
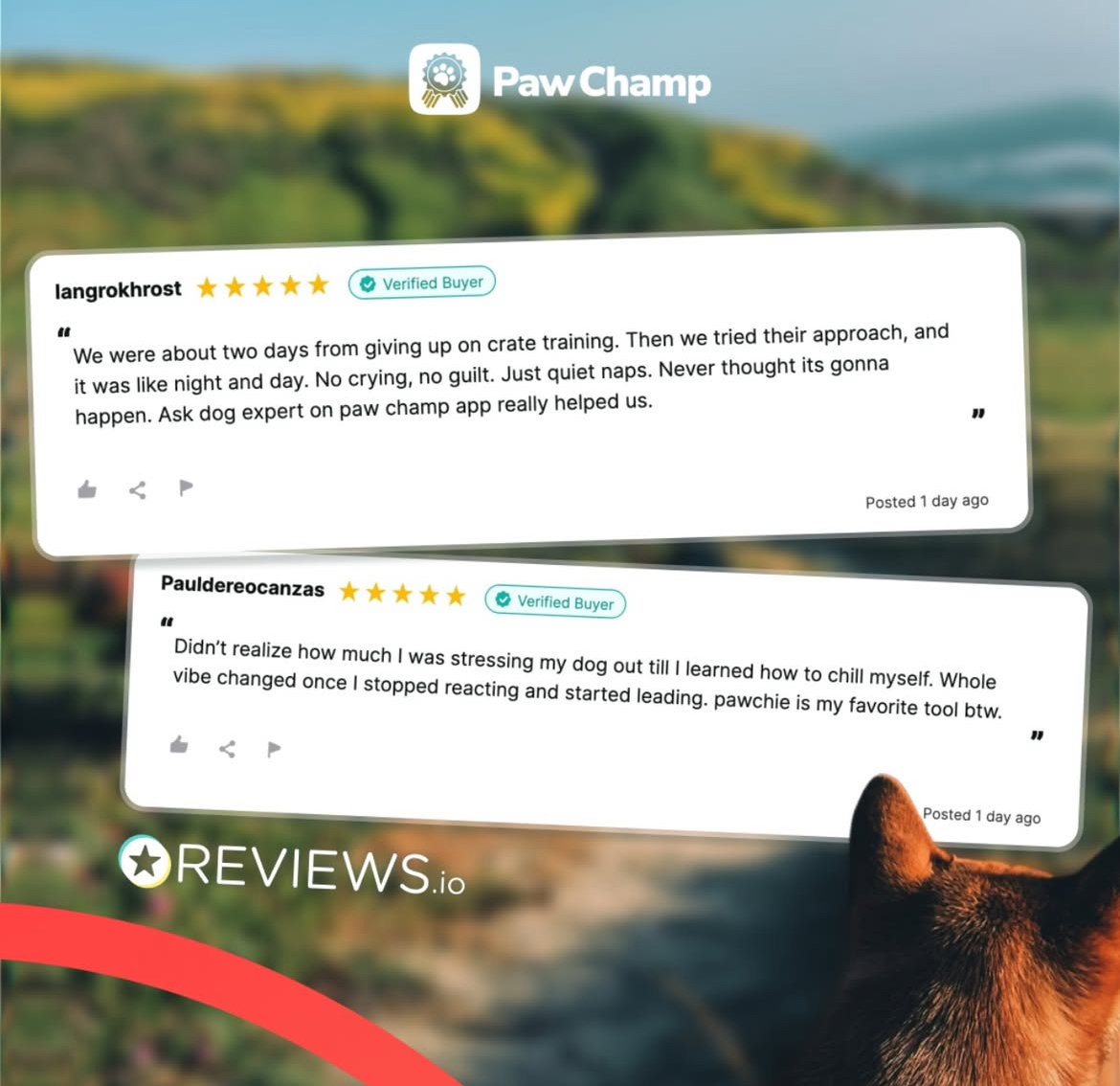
Many owners report:
-
Helpful, compassionate support — Trainers answering questions with calm, practical tips that feel personalized rather than generic.
-
Behavior improvements when consistently applied — Some reviewers say they’ve seen real progress in leash pulling, anxiety, and responsiveness when they stick with the plan.
-
Structured training that’s easy to follow — Users appreciate that lessons are broken into manageable steps and can fit into daily life.