Gastroshiza might not be a term you hear every day, but for many families, it represents a significant medical condition that can impact the start of life. This congenital defect involves the abdominal wall and can lead to various challenges for newborns and their parents. Understanding gastroshiza is crucial for anyone facing this diagnosis or supporting someone who is.
As we dive into this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore what gastroshiza entails, its causes, symptoms, types and how it’s diagnosed and treated. We’ll also discuss life after diagnosis—what it means for both children and their families—as well as current research on gastroshiza that offers hope for better outcomes in the future. Whether you’re seeking information out of curiosity or necessity, you’ll find valuable insights throughout this journey into understanding gastroshiza.
What is Gastroshiza?
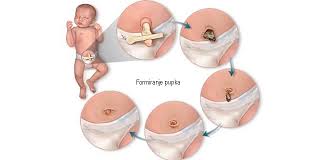
Gastroshiza is a type of congenital abdominal wall defect. It occurs when the abdominal muscles do not fully close during fetal development, leading to a gap, typically located on the right side of the body.
This condition allows organs such as the intestines to protrude outside the abdomen. Unlike other similar defects, gastroshiza does not involve a protective membrane covering these exposed organs.
The exact cause remains unclear, but several factors may contribute to its occurrence. Genetic and environmental influences are believed to play roles in this complex condition.
Babies born with gastroshiza often require immediate medical attention after birth. Surgical intervention is usually necessary to reposition the organs and repair the abdominal wall, ensuring proper functioning as they grow. Understanding this condition can pave the way for better support and care for affected families.
Causes and Symptoms of Gastroshiza
Gastroshiza occurs when the abdominal wall doesn’t fully close during fetal development. This condition allows some of the intestines to protrude outside of the body, typically on one side of the umbilical cord.
The exact cause remains unclear, but genetic and environmental factors may contribute. Some studies suggest that maternal age and certain medications could increase risk.
Symptoms are usually visible at birth. The most apparent sign is an external pouch containing exposed organs like intestines or stomach lining. Infants may face additional challenges such as feeding difficulties or infections.
Early detection through prenatal ultrasounds can help prepare families for what lies ahead. Understanding these aspects can empower parents with knowledge as they navigate this complex situation.
Types of Gastroshiza
Gastroshiza primarily manifests as a defect in the abdominal wall. However, its presentation can vary significantly.
The most common type is referred to as isolated gastroshiza. In this case, the intestines are exposed through an opening in the abdomen without other associated anomalies. This situation allows for focused surgical intervention and management.
Another form includes complex gastroshiza. Here, additional congenital abnormalities may accompany the condition, affecting various organ systems such as cardiac or urinary functions. The complexity necessitates a coordinated approach involving multiple specialists.
There’s also transient gastroshiza observed during early gestation stages. Sometimes, it resolves on its own before birth but requires careful monitoring throughout pregnancy to assess any potential complications.
Understanding these distinctions aids healthcare providers in tailoring treatments specific to each child’s needs while enhancing overall care strategies for families affected by this condition.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
Diagnosing gastroshiza typically begins with imaging tests like ultrasound. This helps visualize the abdominal wall defect and any associated complications. Doctors may also conduct additional scans to assess the baby’s overall health.
Once diagnosed, treatment usually involves surgery shortly after birth. Surgeons work to place the exposed organs back into the abdomen and repair the defect. Timing can vary based on each child’s condition.
Some infants might need a staged approach if their stomach is too small or other issues arise during initial evaluation. In these cases, a temporary protective covering called a silo may be used until surgery can occur safely.
Post-surgery care is crucial for recovery. Babies often require monitoring in a neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) to ensure they heal properly while receiving necessary nutrition through IV or feeding tubes as they recover from surgery.
Life After Gastroshiza: Long-Term Effects and Management
Life after gastroshiza can present unique challenges. Children may face ongoing medical care, including regular check-ups and follow-up surgeries. These are essential for monitoring growth and development.
Nutritional support plays a critical role in management. A tailored diet plan can address specific needs, ensuring the child receives adequate nutrition while minimizing complications.
Parents often find themselves navigating emotional hurdles as well. Support groups can provide valuable resources and connection with others facing similar experiences. Sharing stories helps build resilience.
Physical activities should be encouraged but approached cautiously. Engaging in age-appropriate exercises promotes strength and confidence without overwhelming limitations.
Education about the condition is vital for both parents and children. Understanding gastroshiza fosters advocacy skills that empower families to seek appropriate care throughout their lives.
Regular communication with healthcare providers ensures that any emerging issues are addressed promptly, leading to better long-term outcomes for those affected by gastroshiza.
Coping with a Child with Gastroshiza
Coping with a child diagnosed with gastroshiza can be overwhelming. The journey begins at the moment of diagnosis when parents face an array of emotions.
Creating a support network is essential. Connecting with other families who have experienced similar challenges can provide comfort and insight. Online forums and local support groups are invaluable resources.
Educating yourself about gastroshiza helps in navigating medical decisions. Understanding treatment options, potential complications, and recovery processes empowers parents to advocate for their child’s needs effectively.
Routine appointments may become part of life. Keeping track of health records, medications, and doctor recommendations ensures that you’re always prepared for each visit.
Self-care isn’t selfish; it’s necessary. Parents should carve out time for themselves amidst the chaos. Engaging in hobbies or simply taking breaks can replenish energy levels needed to care for your child fully.
Most importantly, celebrate small victories along the way—each milestone marks progress on this unique journey together.
Current Research and Future Developments
Current research on gastroshiza is focused heavily on improving surgical techniques and enhancing patient outcomes. Innovations in minimally invasive procedures are being explored, aiming to reduce recovery times and complications.
Researchers are also investigating the genetic factors that may contribute to the condition. Understanding these elements could pave the way for targeted therapies or even preventive measures.
In addition, studies are examining nutritional interventions for children diagnosed with gastroshiza. Ensuring proper growth and development remains a priority, as specialized diets can significantly impact health after surgery.
Collaboration between pediatric surgeons and geneticists is increasing. This multidisciplinary approach holds promise for better understanding this complex condition.
Future developments may include advanced imaging technologies that allow earlier diagnosis of gastroshiza, ultimately leading to timely intervention. As awareness grows within medical communities, so does the potential for groundbreaking treatments tailored specifically for affected individuals.
Conclusion
Gastroshiza, a rare congenital defect, requires understanding and compassion. Parents facing this diagnosis need information and support. Awareness of causes, symptoms, and treatment can make navigating this journey easier.
The medical community continues to advance in research, offering hope for improved management strategies. Life after gastroshiza can be challenging but also filled with potential. Each child is unique; their experiences will vary.
Engaging with healthcare providers and support groups fosters resilience in families dealing with gastroshiza. By sharing knowledge and personal stories, we build a network of strength that benefits everyone involved.
As research progresses and treatments improve, the future looks brighter for those affected by gastroshiza—allowing them to lead fulfilling lives while managing their condition effectively.